
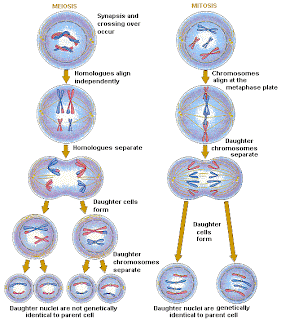
The mitotic cell undergoes prophase only once. No interphase will happen before meiosis II.Īfter interphase, the cell proceeds to prophase, where the nuclear membrane disintegrates, and the chromatin condenses to form the chromosomes. It is only during the reproduction process that such a diploid state is restored in the offspring.īefore undergoing the four phases, the cell first needs to grow and replicate its chromosomes in a preliminary stage called interphase.Ī sex cell will only undergo interphase once. The chromosome number of the resulting daughter cells is reduced by half (becomes haploid, n). The resulting daughter cells are genetically the same because no recombination occurred during the process.įour. Two divisions results to haploid (n) offspring Only one division results to diploid (2n) offspring Meiosis I and II have the same phases as mitosis, which are only different in some events. Meiosis is quite long as it involves two successive divisions that reduce chromosome number.īasically, it is divided into two: meiosis I and meiosis II. Mitosis involves only one cell division that is composed of four major phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In plants, sex cells are located in the pollen in the stamen and egg cells in the pistil. In animals like humans, meiosis takes place in male sperm cells and female egg cells to prepare them for sexual reproduction. Sexual division Meiosis occurs in sex cells or gametes.
#HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES MITOSIS VS MEIOSIS SKIN#
Somatic cells include muscle cells, bone cells, skin cells, nerve cells, etc. Somatic cells (or vegetative cells) are cells that make up the bodies of living organisms, other than the sex cells. Type of cell division and occurs in what type of cellsĪsexual division Mitosis occurs in somatic cells.
If the nuclear envelope was re-made after telophase I, it will break down again.The steps of meiosis II are summarised below: a) Prophase II

The homologous chromosomes are separated from each other and assorted into two diploid daughter cells.ĭuring meiosis II, the two diploid daughter cells divide in order to produce a total of four haploid daughter cells, each with a single copy of every chromosome (only 23 chromosomes total per cell). The remainder of meiosis I is exactly the same as mitosis. Two diploid daughter cells are produced.
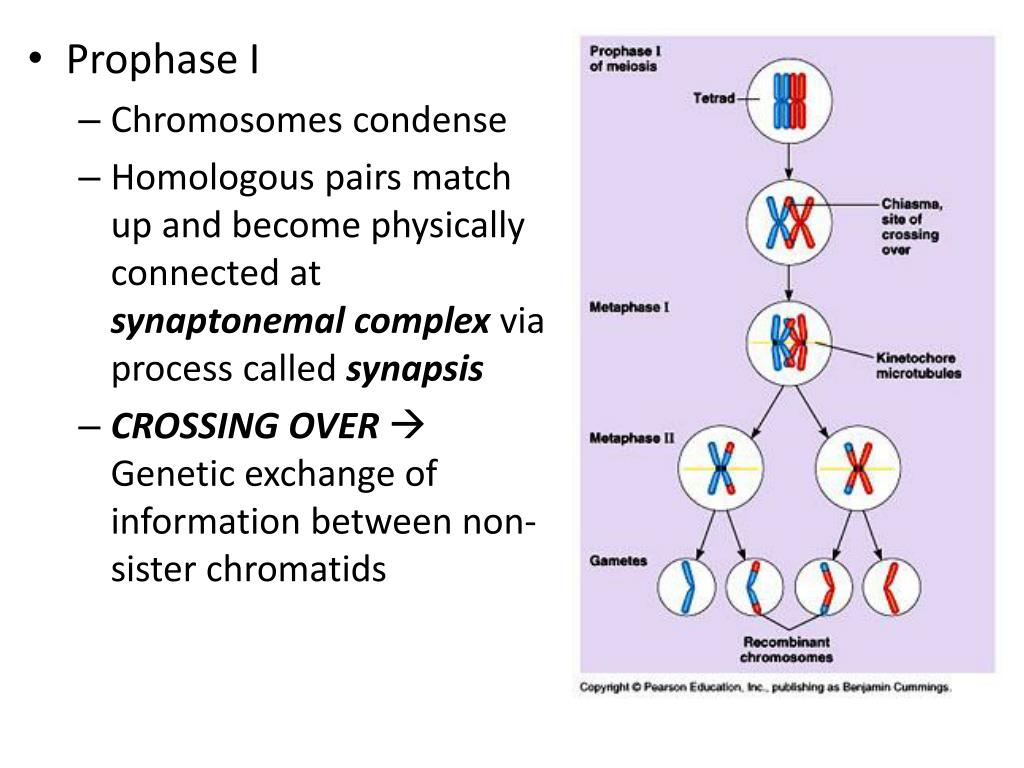
During meiosis I, a very important event known as crossing over occurs during prophase I. Each of the phases of meiosis I are the same as normal mitosis, except we refer to them as prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I. Meiosis I results in the production of two diploid daughter cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
